Additive vs multiplicative effect modification ideas
Home » modification » Additive vs multiplicative effect modification ideasYour Additive vs multiplicative effect modification images are ready. Additive vs multiplicative effect modification are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Additive vs multiplicative effect modification files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for additive vs multiplicative effect modification images information linked to the additive vs multiplicative effect modification interest, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site always provides you with hints for downloading the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Additive Vs Multiplicative Effect Modification. We will explain additive and multiplicative interaction effects and compare their strengths and context of use. This quantity measures the extent to which on the risk ratio scale the effect of both exposures together exceeds the product of the effects of the two exposures considered separately. From the perspective of public health and clinical decision making the additive scale is usually considered most appropriate. Finally we will demonstrate the relevant analytical procedures using.
 Confounding And Interaction Part Ii Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
Confounding And Interaction Part Ii Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
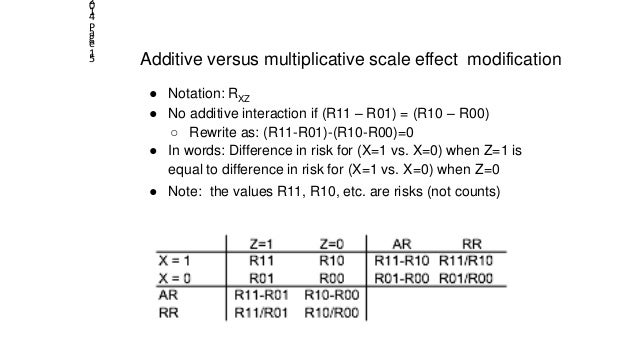
Multivariable methods can also be used to assess effect modification. In addition we will introduce a four-step approach to present analyses of effect modification and interaction in research articles. Additive versus multiplicative scale effect modification Notation. Both approaches are based on regression methods. The data have. Interaction Effect Modification Interaction should be assessed in terms of a departure from additive effects this requires an additive model ie.
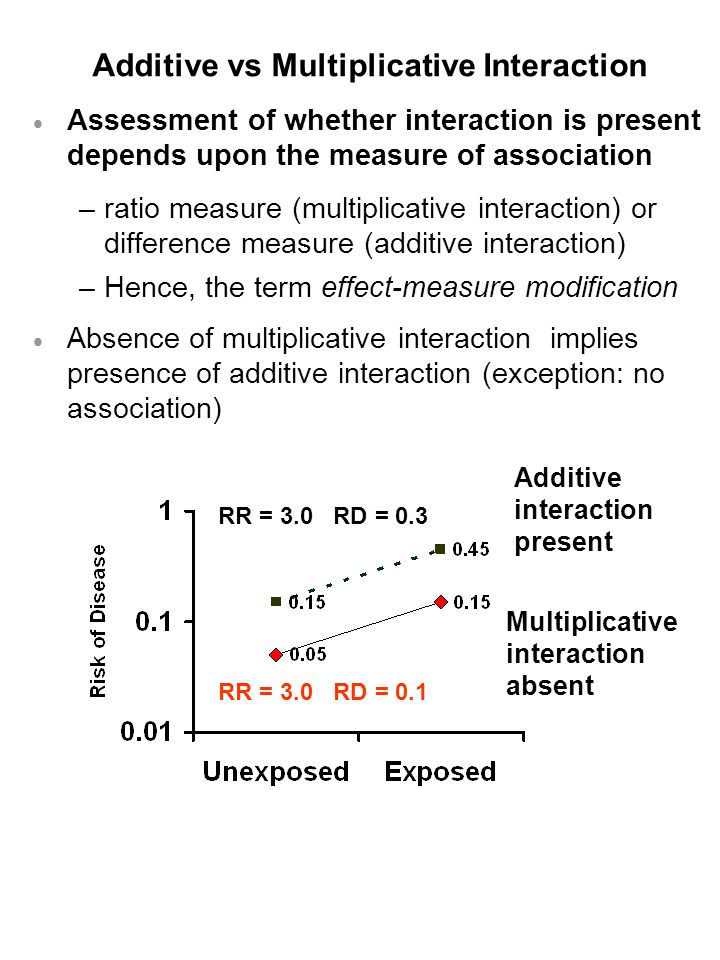
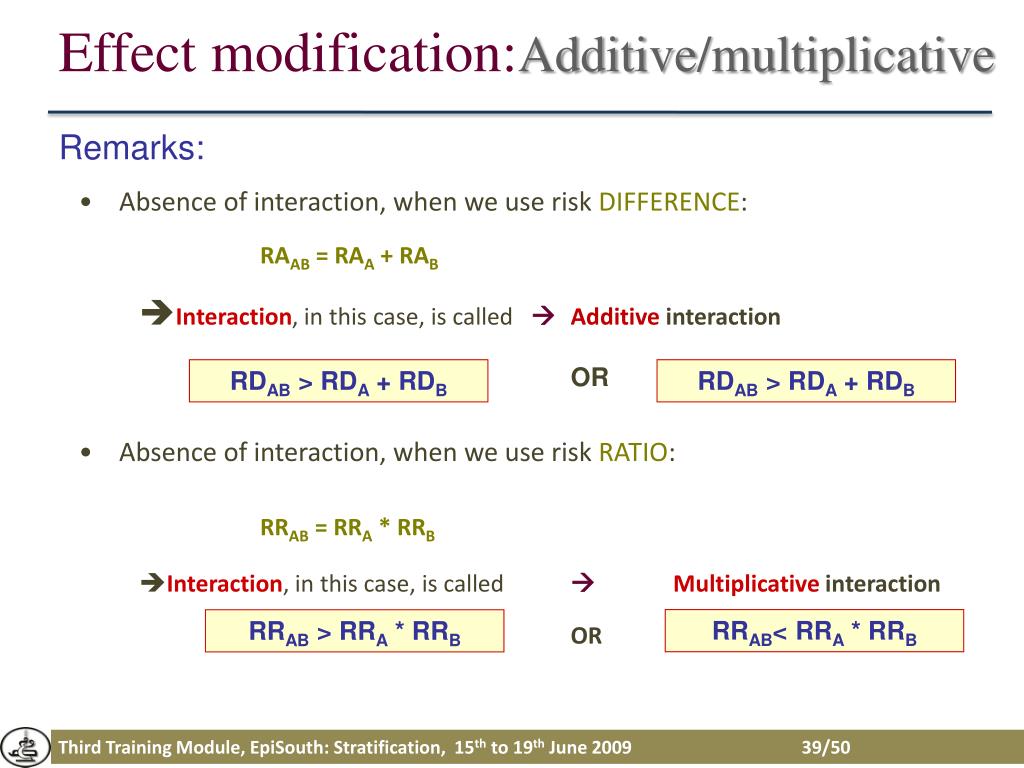
On an additive scale based on risk differences RD or on a multiplicative scale based on relative risks RR.
Previous124 - Interaction Revisited. Previous124 - Interaction Revisited. This is well known in the epidemiology literature but not well enough know among biostatisticians 2. Effect modification can be additive or multiplicative. Effect modification is something we want to highlight in our results not something to be adjusted away. This quantity measures the extent to which on the risk ratio scale the effect of both exposures together exceeds the product of the effects of the two exposures considered separately.

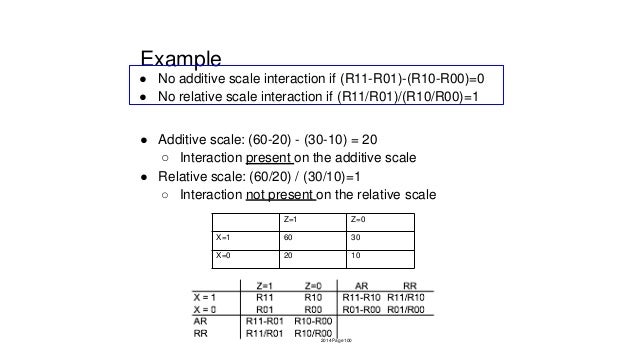
Heterogeneity of effects b. We will explain additive and multiplicative interaction effects and compare their strengths and context of use. RXZ No multiplicative interaction if R11R01R10R00 Rewrite as. Finally we will demonstrate the relevant analytical procedures using. In addition we will introduce a four-step approach to present analyses of effect modification and interaction in research articles.

Effect modification can be measured in two ways. Ratio of risksrates when X1 vs. This quantity measures the extent to which on the risk ratio scale the effect of both exposures together exceeds the product of the effects of the two exposures considered separately. Additional multiplicative change in the odds ratio beyond the smoking or coffee drinking effect alone when you have both of these risk factors present i i i i i i coffee smoke coffee smoke p p 1 0 1 2 3. If RR 11ðRR 10RR 01Þ 1 the multiplicative interaction is said to be positive.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Both approaches are based on regression methods. Effect varies across subgroups Statistical Interaction Deviation from a specified model form additive or multiplicative Often used interchangeably. Figure 76 should make it clear exactly how these work. Previous124 - Interaction Revisited. The data have.
 Source: sphweb.bumc.bu.edu
Source: sphweb.bumc.bu.edu
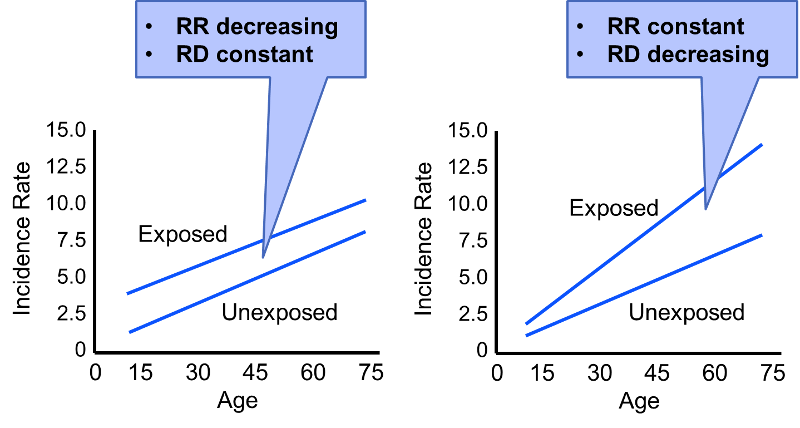
A risk difference measure There are several reasons why it is generally preferable to use a multiplicative model ie. X0 when Z1 is equal to ratio of risksrates when X1 vs. Additive versus multiplicative scale effect modification Notation. Additional multiplicative change in the odds ratio beyond the smoking or coffee drinking effect alone when you have both of these risk factors present i i i i i i coffee smoke coffee smoke p p 1 0 1 2 3. Assessing EMMstatistical interaction a.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Case for smokers -vs-non-smokers is multiplied for coffee drinkers as compared to non-coffee drinkers COMMON IDEA. For investigating disease etiology the multiplicative model is often more relevant. I have discussed in an article that perhaps the time has come when we need to reconsider if there can be such a thing as additive versus multiplicative effect modification for binary outcomes. Additive versus multiplicative scale effect modification Notation. Finally we will demonstrate the relevant analytical procedures using.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The effect of one variable on the outcome depends on the levels of another variable. Effect measure modification 2. From the perspective of public health and clinical decision making the additive scale is usually considered most appropriate. I have discussed in an article that perhaps the time has come when we need to reconsider if there can be such a thing as additive versus multiplicative effect modification for binary outcomes. Effect modification is something we want to highlight in our results not something to be adjusted away.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
For investigating disease etiology the multiplicative model is often more relevant. The data have. X0 when Z0 2014 Page 16 17. Effect modification is something we want to highlight in our results not something to be adjusted away. Ratio of risksrates when X1 vs.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Previous124 - Interaction Revisited. X0 when Z0 2014 Page 16 17. Depends upon the scale additive or multiplicative. Figure 76 should make it clear exactly how these work. Case for smokers -vs-non-smokers is multiplied for coffee drinkers as compared to non-coffee drinkers COMMON IDEA.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Heterogeneity of effects b. Effect varies across subgroups Statistical Interaction Deviation from a specified model form additive or multiplicative Often used interchangeably. X0 when Z1 is equal to ratio of risksrates when X1 vs. In addition we will introduce a four-step approach to present analyses of effect modification and interaction in research articles. Effect modification can be additive or multiplicative.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
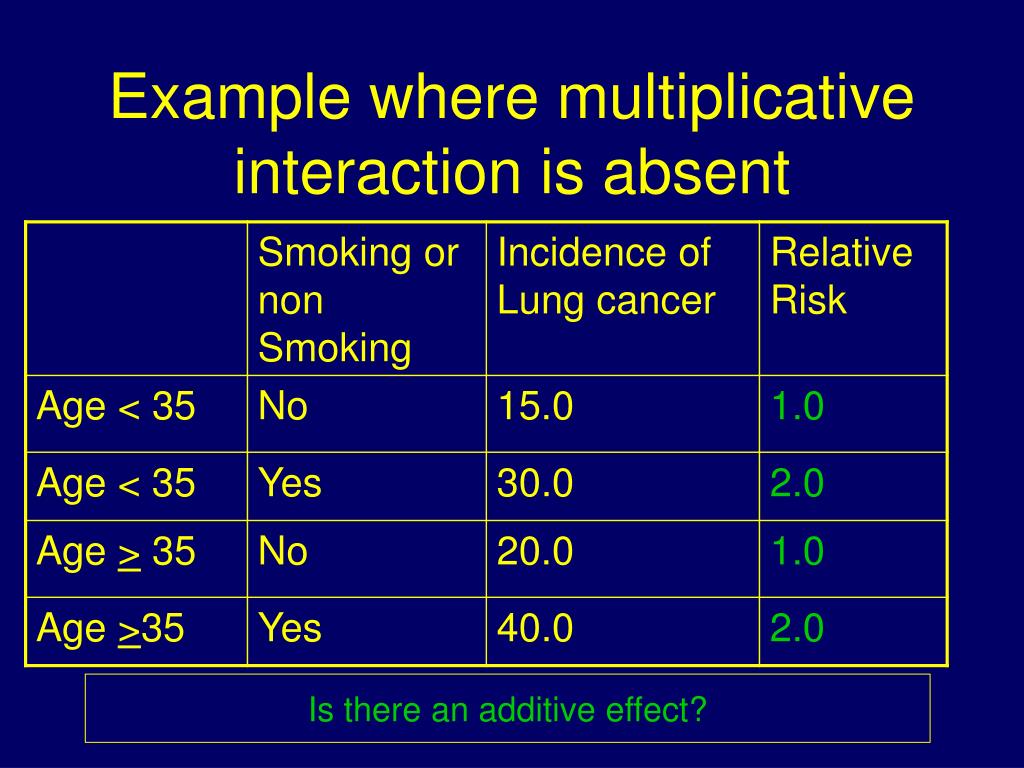
In other words the effects of smoking and asbestos were not just additive they were multiplicative. Multiplicative effect modification interaction The name for these concepts differs depending on the field you work in. If RR 11ðRR 10RR 01Þ 1 the multiplicative interaction is said to be positive. How Different is Different. Additional multiplicative change in the odds ratio beyond the smoking or coffee drinking effect alone when you have both of these risk factors present i i i i i i coffee smoke coffee smoke p p 1 0 1 2 3.

P 11 - p 10 - p 01 p 00 010 - 004 - 005 002 003 0 Multiplicative. Effect measure modification 2. X0 when Z1 is equal to ratio of risksrates when X1 vs. Effect modification can be additive or multiplicative. For addressing public health measures to reduce disease frequency an additive model is more relevant.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
For investigating disease etiology the multiplicative model is often more relevant. Choose an effect modification model that is important to the research objectives. In additive models the risk of disease has an additive form that generally uses linear regression while multiplicative models use logistic. Effect modification is something we want to highlight in our results not something to be adjusted away. Ratio of risksrates when X1 vs.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
In other words the effects of smoking and asbestos were not just additive they were multiplicative. Effect modification Or more precisely effect- measure modification Heterogeneity of effects Subgroup effects ie. This quantity measures the extent to which on the risk ratio scale the effect of both exposures together exceeds the product of the effects of the two exposures considered separately. Unlike for confounding where a 10 change from crude to adjusted is an accepted definition for confounding there exists no such standardized definition for how different the stratum-specific measures must be to. X0 when Z0 2014 Page 16 17.

Heterogeneity of effects b. Finally we will demonstrate the relevant analytical procedures using. Figure 76 should make it clear exactly how these work. A risk difference measure There are several reasons why it is generally preferable to use a multiplicative model ie. Case for smokers -vs-non-smokers is multiplied for coffee drinkers as compared to non-coffee drinkers COMMON IDEA.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
This is well known in the epidemiology literature but not well enough know among biostatisticians 2. Unlike for confounding where a 10 change from crude to adjusted is an accepted definition for confounding there exists no such standardized definition for how different the stratum-specific measures must be to. X0 when Z0 2014 Page 16 17. Additive versus multiplicative scale effect modification Notation. For investigating disease etiology the multiplicative model is often more relevant.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
For addressing public health measures to reduce disease frequency an additive model is more relevant. Effect measure modification 2. X0 when Z1 is equal to ratio of risksrates when X1 vs. I have discussed in an article that perhaps the time has come when we need to reconsider if there can be such a thing as additive versus multiplicative effect modification for binary outcomes. Finally we will demonstrate the relevant analytical procedures using.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Multiplicative effect modification interaction The name for these concepts differs depending on the field you work in. Figure 76 should make it clear exactly how these work. How Different is Different. Effect modification Or more precisely effect- measure modification Heterogeneity of effects Subgroup effects ie. Additive versus multiplicative scale effect modification Notation.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
How Different is Different. Finally we will demonstrate the relevant analytical procedures using. How Different is Different. Effect modification is something we want to highlight in our results not something to be adjusted away. Interaction Effect Modification Interaction should be assessed in terms of a departure from additive effects this requires an additive model ie.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title additive vs multiplicative effect modification by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
Category
Related By Category
- Leatherman modification ideas
- Organizational behavior modification theory ideas
- Seamoth modification station location information
- Custody modification reasons information
- Kak shockwave modification information
- Subnautica cant place vehicle modification station information
- Loan modification while in chapter 13 information
- Behavior modification is based upon the principles of rewards and punishments advanced by ideas
- Modification lawyer information
- Z4 modification information