Effect modification vs confounding examples ideas in 2023
Home » modification » Effect modification vs confounding examples ideas in 2023Your Effect modification vs confounding examples images are available in this site. Effect modification vs confounding examples are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Effect modification vs confounding examples files here. Find and Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re looking for effect modification vs confounding examples images information linked to the effect modification vs confounding examples interest, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site always gives you suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more informative video content and graphics that match your interests.
Effect Modification Vs Confounding Examples. 1 If the stratum-specific estimates differ from one another and they are both less than the crude estimate or if they are both greater than the crude estimate then there is both confounding and effect modification. A variable that differentially positively and negatively modifies the observed effect. Whereas effect modifiers are those that also cause an apparent. Positiveconfounding when the observed association is biased away from the null and negativeconfounding when the observed association is biased toward the null both occur.
 Confounding Effect Page 1 Line 17qq Com From line.17qq.com
Confounding Effect Page 1 Line 17qq Com From line.17qq.com
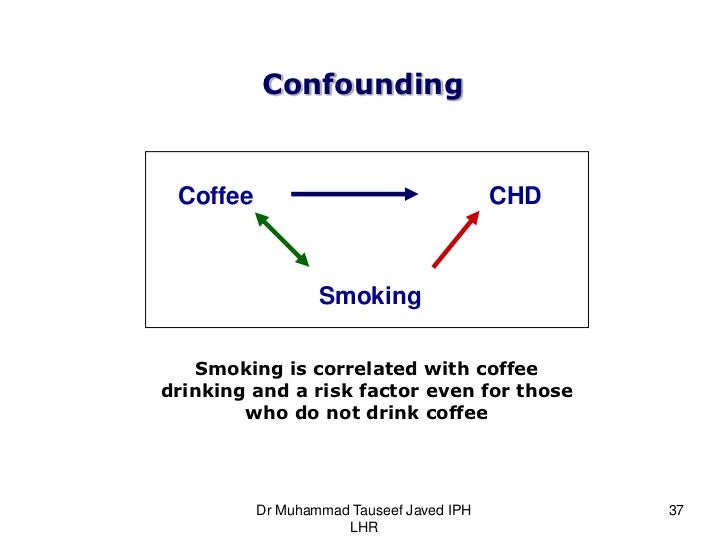
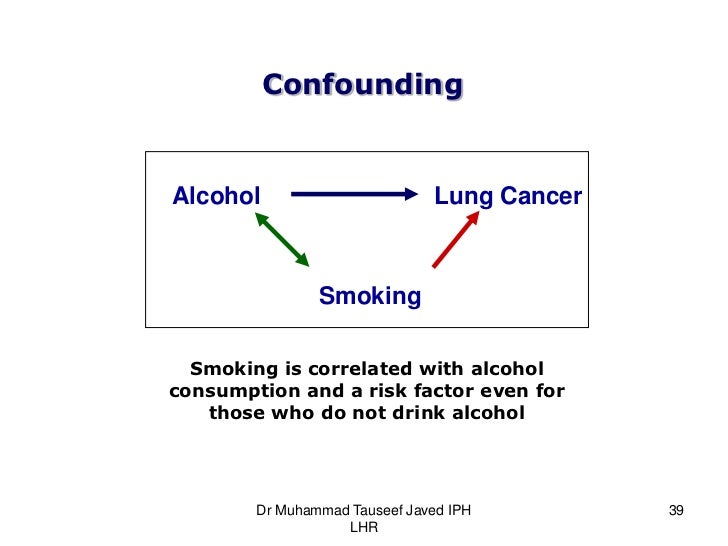
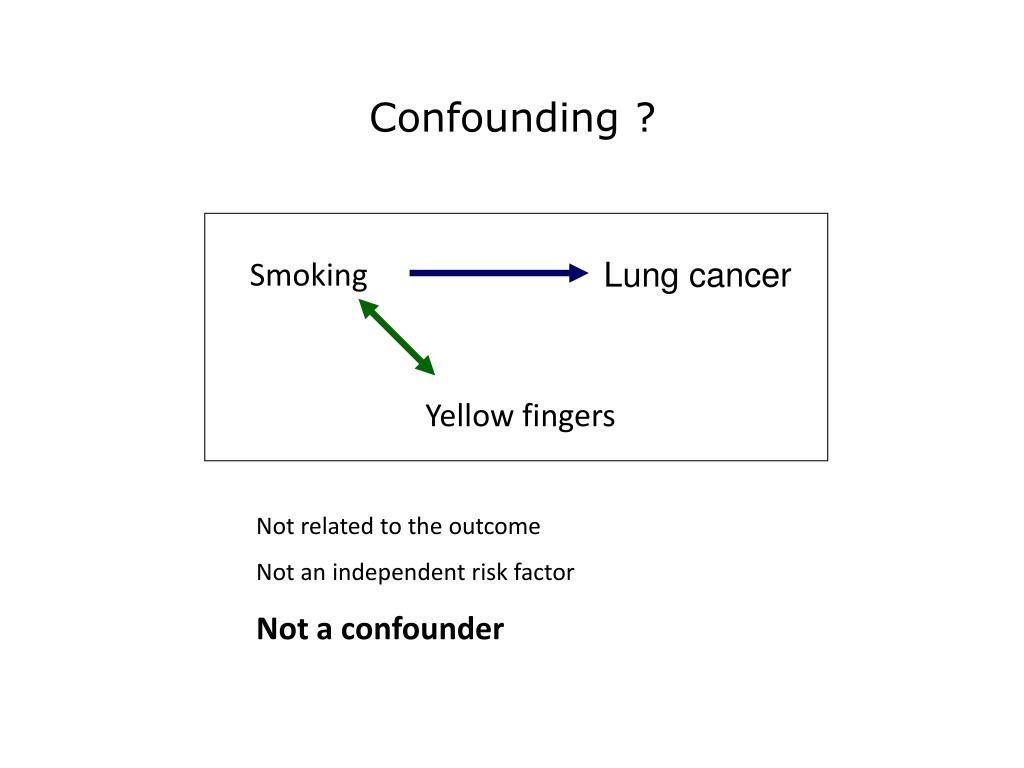
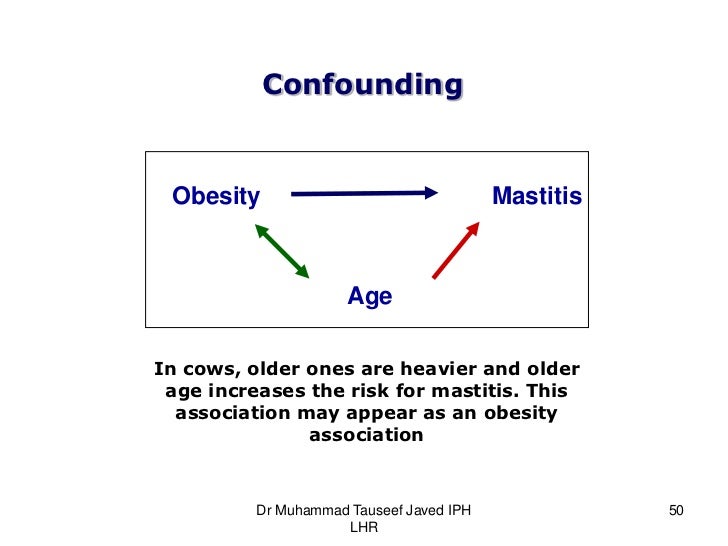
Smoking and exposure to asbestos are both risk factors for lung cancer. A variable that differentially positively and negatively modifies the observed effect. Effect Modification and Confounding in logistic. Crude RR 1276183514862681 125 120 132 Denied Admitted 1835 2681 Female Male 1276 1486 559 1195. For example imagine you are testing out a new treatment that has come onto the market Drug X. Suppose that the smokers are much older than the non- smokers We know that age is a risk factor for heart disease - Implies the RR2 is really reflecting the mixture of two effects Older age and smoking.
I have always struggled with confounding and effect modification.
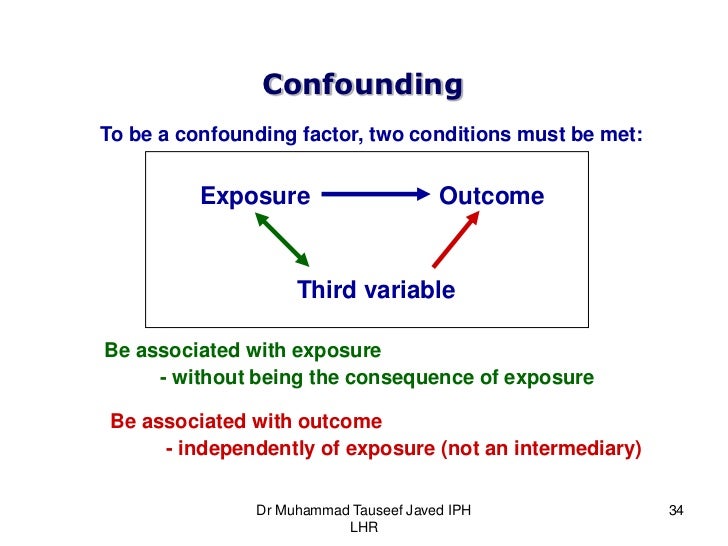
Examples from the literature 1651 Confounding versus effect modification. Crude RR 1276183514862681 125 120 132 Denied Admitted 1835 2681 Female Male 1276 1486 559 1195. I know the definition confounders are extraneous variable that cause apparent association between exposure and outcome when none exists because the confounders are related to both the exposure and the outcome. Effect modifier Belongs to nature Different effects in different strata Simple Useful Increases knowledge of biological mechanism Allows targeting of PH action Confounding factor Belongs to study Stratefied OR different from crude OR Distortion of effect Creates confusion in data Prevent in protocol phase. Differences between Confounding and Effect Modification With confounding youre initially getting the wrong answer because the confounder is not distributed evenly between your groups. One classic example of effect modification is smoking which is an effect modifier for exposure to asbestos and lung cancer.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
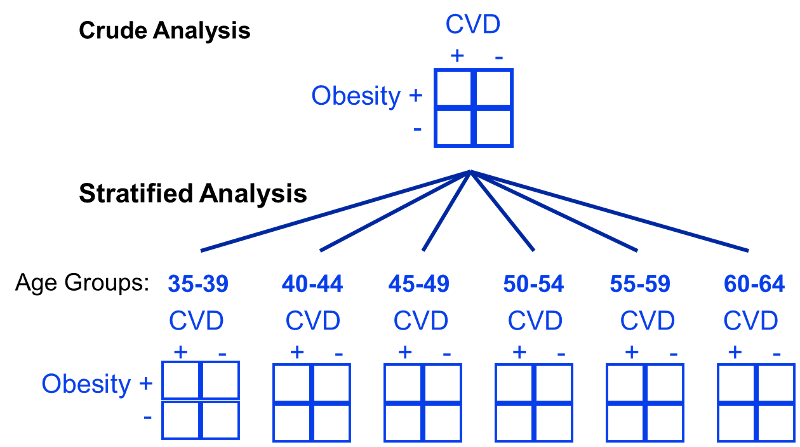
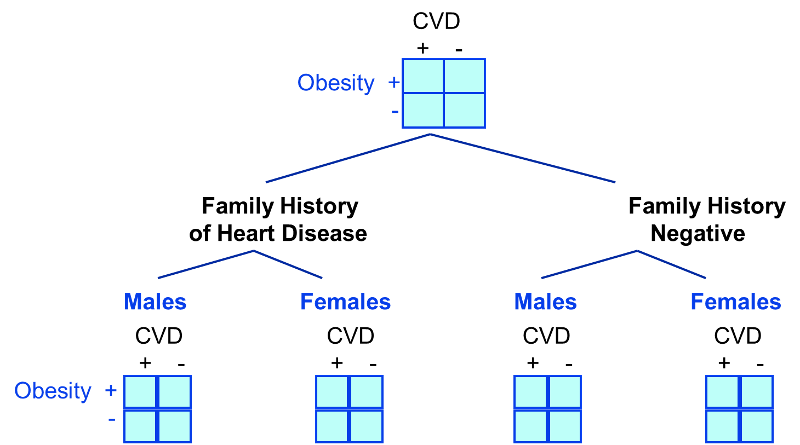
If there is both effect modification and confounding. Having bigger feet is associated with reading speed only because of confounding by grade level. Contrast with confounding Effect modification A more detailed description of the true relationship between the exposure and the outcome Effect modification is a finding to be reported even celebrated not a bias to be eliminated Effect modification is a natural phenomenon that exists independently of the study design The presence and interpretation of effect modification depends upon the choice of effect measure ratio vs. Effect modification occurs when the strength of an association between an exposure and an outcome differs according to the level of another variable. Lets revisit the Berkeley study.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
1 If the stratum-specific estimates differ from one another and they are both less than the crude estimate or if they are both greater than the crude estimate then there is both confounding and effect modification. A situation in which the effect or association between an exposure and outcome is distorted by the presence of another variable. For example imagine you are testing out a new treatment that has come onto the market Drug X. Lets revisit the Berkeley study. Tree damage and elevation example 1521 Effect modification.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Smoking and exposure to asbestos are both risk factors for lung cancer. Lets revisit the Berkeley study. A variable that differentially positively and negatively modifies the observed effect. Effect Modification Confounding Bias overall because treatment groups differ by a relevant characteristic Persons taking vitamin D appear less frail because they have more resources to protect their health Addressed by computing effects in comparable people vit D effect in persons with equal resources Effect modification. Positiveconfounding when the observed association is biased away from the null and negativeconfounding when the observed association is biased toward the null both occur.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
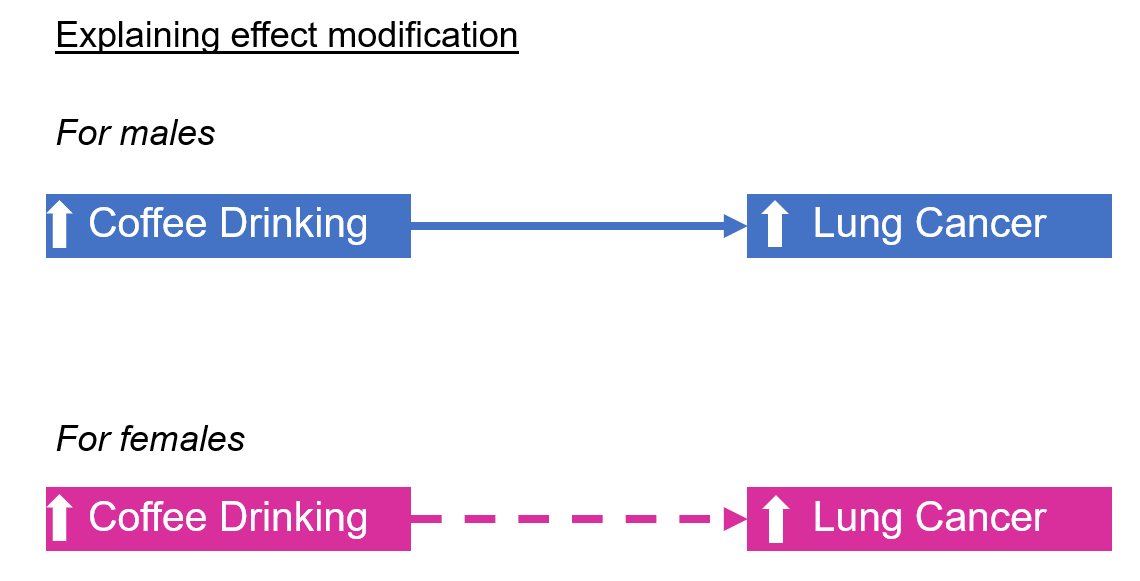
Matching randomization Control in analysis phase. Coffee drinking gender coffee drinking gender - lung cancer. Effect modifier Belongs to nature Different effects in different strata Simple Useful Increases knowledge of biological mechanism Allows targeting of PH action Confounding factor Belongs to study Stratefied OR different from crude OR Distortion of effect Creates confusion in data Prevent in protocol phase. Lets revisit the Berkeley study. Suppose that the smokers are much older than the non- smokers We know that age is a risk factor for heart disease - Implies the RR2 is really reflecting the mixture of two effects Older age and smoking.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Contrast with confounding Effect modification A more detailed description of the true relationship between the exposure and the outcome Effect modification is a finding to be reported even celebrated not a bias to be eliminated Effect modification is a natural phenomenon that exists independently of the study design The presence and interpretation of effect modification depends upon the choice of effect measure ratio vs. 1 If the stratum-specific estimates differ from one another and they are both less than the crude estimate or if they are both greater than the crude estimate then there is both confounding and effect modification. Crude RR 1276183514862681 125 120 132 Denied Admitted 1835 2681 Female Male 1276 1486 559 1195. Confounding occurs when a factor is associated with both the exposure and the outcome but does not lie on the causative pathway. Here you need to consider two possibilities.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Example Mean SAT scores were compared for the 50 US states. Suppose that the smokers are much older than the non- smokers We know that age is a risk factor for heart disease - Implies the RR2 is really reflecting the mixture of two effects Older age and smoking. A situation in which the effect or association between an exposure and outcome is distorted by the presence of another variable. Differences between Confounding and Effect Modification With confounding youre initially getting the wrong answer because the confounder is not distributed evenly between your groups. For example imagine you are testing out a new treatment that has come onto the market Drug X.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Whereas effect modifiers are those that also cause an apparent. Confounding occurs when a factor is associated with both the exposure and the outcome but does not lie on the causative pathway. Confusion regarding effect modification is further exacerbated by a lack of consensus on both semantic and conceptual issues Joseph KS. 1 If the stratum-specific estimates differ from one another and they are both less than the crude estimate or if they are both greater than the crude estimate then there is both confounding and effect modification. Another good example is the effect of smoking on risk of lung cancer.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Positive confounding when the observed association is biased away from the null and negative confounding when the observed association is biased toward the null both occur. Smoking and exposure to asbestos are both risk factors for lung cancer. Controlling for confounding by stratification. If Drug X works in females but does not work in males this is an example of effect modification. Positiveconfounding when the observed association is biased away from the null and negativeconfounding when the observed association is biased toward the null both occur.
 Source: sphweb.bumc.bu.edu
Source: sphweb.bumc.bu.edu
Contrast with confounding Effect modification A more detailed description of the true relationship between the exposure and the outcome Effect modification is a finding to be reported even celebrated not a bias to be eliminated Effect modification is a natural phenomenon that exists independently of the study design The presence and interpretation of effect modification depends upon the choice of effect measure ratio vs. Here you need to consider two possibilities. One way is to add an interaction term to the regression model. The goal of the study was to compare overall SAT scores using state-wide predictors such as per-pupil expenditures average teacherssalary. One classic example of effect modification is smoking which is an effect modifier for exposure to asbestos and lung cancer.
 Source: line.17qq.com
Source: line.17qq.com
I have always struggled with confounding and effect modification. The goal of the study was to compare overall SAT scores using state-wide predictors such as per-pupil expenditures average teacherssalary. Coffee drinking gender coffee drinking gender - lung cancer. Matching is often used in case-control studies and it has much the same effect as restriction in controlling confounding. 1 If the stratum-specific estimates differ from one another and they are both less than the crude estimate or if they are both greater than the crude estimate then there is both confounding and effect modification.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
Effect Modification and Confounding in logistic. One classic example of effect modification is smoking which is an effect modifier for exposure to asbestos and lung cancer. If Drug X works in females but does not work in males this is an example of effect modification. Here you need to consider two possibilities. Smoking and exposure to asbestos are both risk factors for lung cancer.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
Matching is often used in case-control studies and it has much the same effect as restriction in controlling confounding. Effect Modification and Confounding in logistic. This distorts the measure of association that you calculate remember. Effect Modification Confounding Bias overall because treatment groups differ by a relevant characteristic Persons taking vitamin D appear less frail because they have more resources to protect their health Addressed by computing effects in comparable people vit D effect in persons with equal resources Effect modification. Here you need to consider two possibilities.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Suppose that the smokers are much older than the non- smokers We know that age is a risk factor for heart disease - Implies the RR2 is really reflecting the mixture of two effects Older age and smoking. Having bigger feet is associated with reading speed only because of confounding by grade level. Positive confounding when the observed association is biased away from the null and negative confounding when the observed association is biased toward the null both occur. Effect modification occurs when the strength of an association between an exposure and an outcome differs according to the level of another variable. I know the definition confounders are extraneous variable that cause apparent association between exposure and outcome when none exists because the confounders are related to both the exposure and the outcome.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
One way is to add an interaction term to the regression model. Positiveconfounding when the observed association is biased away from the null and negativeconfounding when the observed association is biased toward the null both occur. Whereas effect modifiers are those that also cause an apparent. Matching randomization Control in analysis phase. Confounding occurs when a factor is associated with both the exposure and the outcome but does not lie on the causative pathway.
 Source: line.17qq.com
Source: line.17qq.com
Matching is often used in case-control studies and it has much the same effect as restriction in controlling confounding. Coffee drinking gender coffee drinking gender - lung cancer. Effect modifier Belongs to nature Different effects in different strata Simple Useful Increases knowledge of biological mechanism Allows targeting of PH action Confounding factor Belongs to study Stratefied OR different from crude OR Distortion of effect Creates confusion in data Prevent in protocol phase. Positive confounding when the observed association is biased away from the null and negative confounding when the observed association is biased toward the null both occur. I know the definition confounders are extraneous variable that cause apparent association between exposure and outcome when none exists because the confounders are related to both the exposure and the outcome.
 Source: jclinepi.com
Source: jclinepi.com
Effect Modification and Confounding in logistic. A situation in which the effect or association between an exposure and outcome is distorted by the presence of another variable. Matching is often used in case-control studies and it has much the same effect as restriction in controlling confounding. This is an example of effect modification or interaction. Whereas effect modifiers are those that also cause an apparent.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
If there is both effect modification and confounding. Introduction to effect modification leaves some students of epidemiology struggling with the distinction between this and the other third variable phenomenon namely confounding. If there is both effect modification and confounding. This distorts the measure of association that you calculate remember. Controlling for confounding by stratification.
 Source: sphweb.bumc.bu.edu
Source: sphweb.bumc.bu.edu
One classic example of effect modification is smoking which is an effect modifier for exposure to asbestos and lung cancer. Examples from the literature 1651 Confounding versus effect modification. In R it can be implemented with the following code. Suppose that the smokers are much older than the non- smokers We know that age is a risk factor for heart disease - Implies the RR2 is really reflecting the mixture of two effects Older age and smoking. Confusion regarding effect modification is further exacerbated by a lack of consensus on both semantic and conceptual issues Joseph KS.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title effect modification vs confounding examples by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
Category
Related By Category
- Leatherman modification ideas
- Organizational behavior modification theory ideas
- Seamoth modification station location information
- Custody modification reasons information
- Kak shockwave modification information
- Subnautica cant place vehicle modification station information
- Loan modification while in chapter 13 information
- Behavior modification is based upon the principles of rewards and punishments advanced by ideas
- Modification lawyer information
- Z4 modification information