Which of the following is a post translational modification of a polypeptide ideas
Home » modification » Which of the following is a post translational modification of a polypeptide ideasYour Which of the following is a post translational modification of a polypeptide images are available. Which of the following is a post translational modification of a polypeptide are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Which of the following is a post translational modification of a polypeptide files here. Download all royalty-free images.
If you’re looking for which of the following is a post translational modification of a polypeptide pictures information linked to the which of the following is a post translational modification of a polypeptide keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our website always provides you with suggestions for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly search and locate more enlightening video content and images that match your interests.
Which Of The Following Is A Post Translational Modification Of A Polypeptide. Polypeptide Chains Can Be Cleaved To Produce A Shorter And Functional Polypeptide. In the human body these PTMs increases the diversity and accuracy of proteins. Post translational modifications or PTMs are involved in modifying the protein structure after they have been translated according to information on the mRNA. All Of The Following Are Examples Of Posttranslational Modifications EXCEPT_____.
 Post Translational Modification Wikiwand From wikiwand.com
Post Translational Modification Wikiwand From wikiwand.com
Which Of The Following Is Not A Type Of Post-translational Modification Or Regulation. Cleavage of a polypeptide into two or more chains During translation amino. Which of the following is a post-translational modification of a polypeptide. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. Post-translational modifications change the chemical nature of the polypeptide chain through alterations to amino acid residues. All Of The Following Are Examples Of Posttranslational Modifications EXCEPT_____.
During translation 20 different amino acids can be incorporated to make up a polypeptide chain.
Post-translational modification PTM refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. Addition of a Disulfide Bridge B. Removal of non-functional Introns D. Another common post-translational modification is cleavage or linking of parts of the protein itself. The N-terminal Amino Acid Is Often Removed Or Modified. Formation of polyribosomes that allows simultaneous formation of many polypeptides from one mRNA transcript D.
 Source: rockland-inc.com
Source: rockland-inc.com
Cleavage of a polypeptide into two or more chains B. Which Of The Following Is Not A Type Of Post-translational Modification Or Regulation. Types Of Post Translational Modifications. The formation of disulfide bonds from cysteine residues may also be referred to as a post-translational modification. Post-translational modifications change the chemical nature of the polypeptide chain through alterations to amino acid residues.
 Source: thermofisher.com
Source: thermofisher.com
Which of the following is a post-translational modification of a polypeptide. A protein is made up of a chain of amino acids also known as a polypeptide. Another common post-translational modification is cleavage or linking of parts of the protein itself. During translation 20 different amino acids can be incorporated to make up a polypeptide chain. In this lesson well talk about some of these modifications and why they help specify or change a.
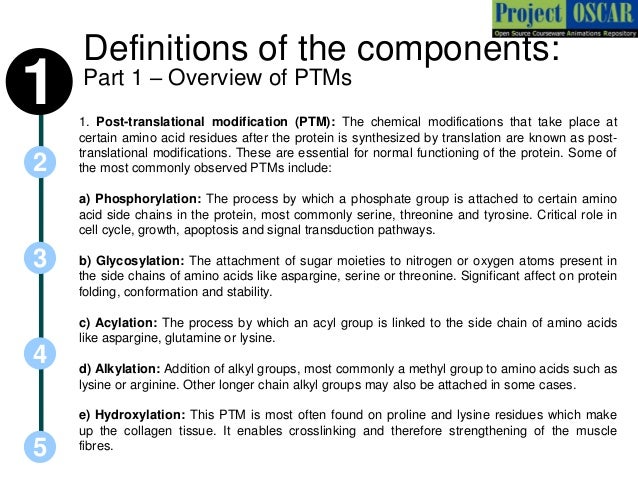 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Post-translational modification PTM is a process in protein biosynthesis that occurs after a protein has been translated from ribonucleic acid The process of translation involves creating a chain of amino acids that corresponds to the RNA template. Which of the following would NOT be a post-translational modification. Removal of non-functional Introns D. Signal-peptides may be cleaved parts may be excised from the middle of the protein or new covalent linkages may be made between cysteine or other amino acid side chains. During translation 20 different amino acids can be incorporated to make up a polypeptide chain.
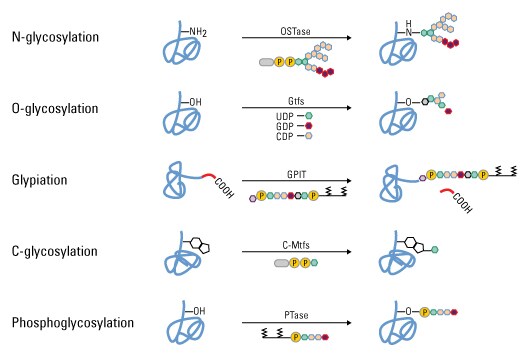 Source: thermofisher.com
Source: thermofisher.com
During translation 20 different amino acids can be incorporated to make up a polypeptide chain. Which Of The Following Is Not A Type Of Post-translational Modification Or Regulation. Removal of non-functional Introns D. A protein is made up of a chain of amino acids also known as a polypeptide. Types Of Post Translational Modifications.
 Source: mcponline.org
Source: mcponline.org
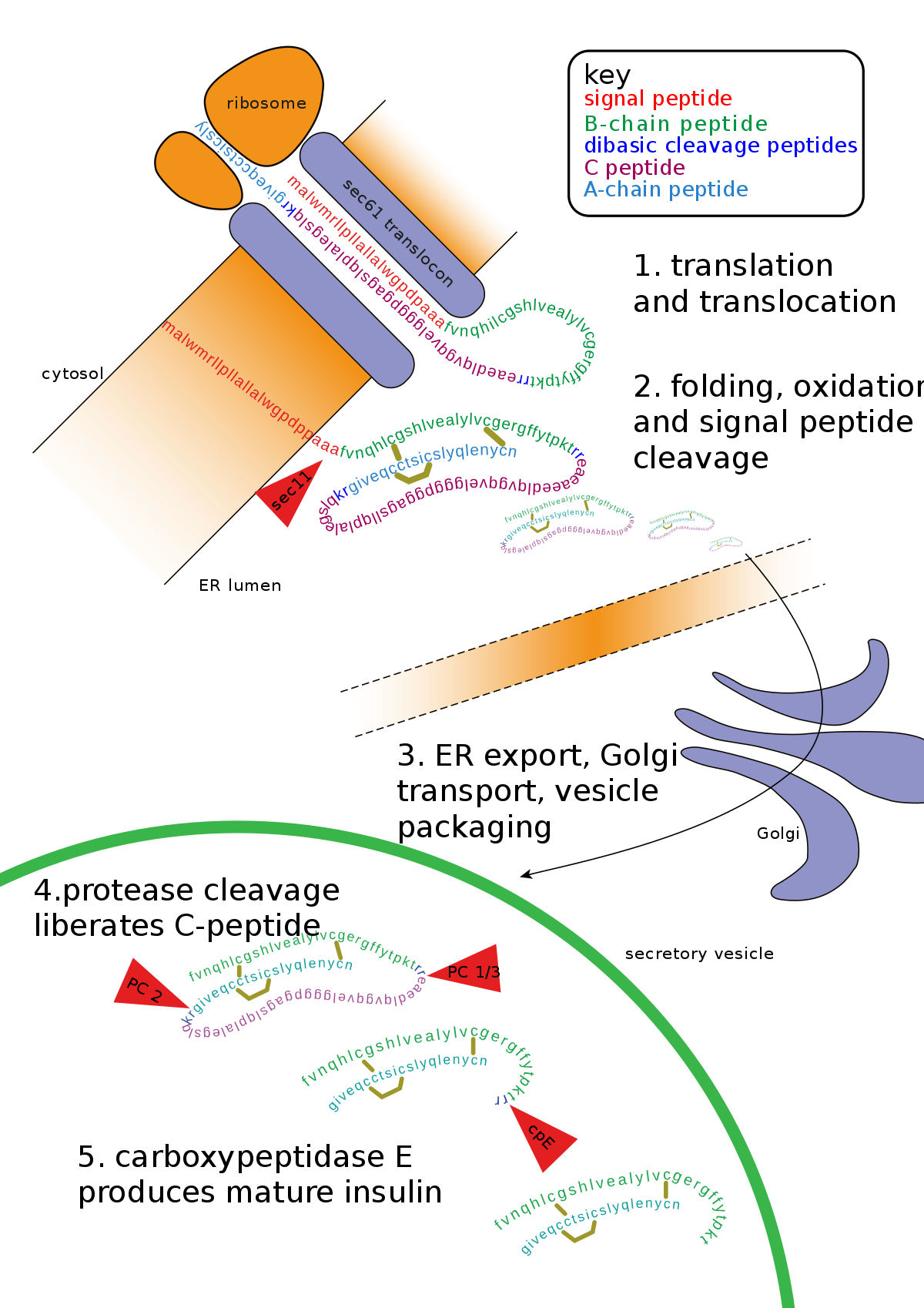
During translation about 30-40 polypeptide residues are relatively protected by the ribosome tunnel T and exit sites E1 and E2 in the large subunit. Post-translational modifications take place in the ER and include folding glycosylation multimeric protein assembly and proteolytic cleavage leading to. During translation 20 different amino acids can be incorporated to make up a polypeptide chain. After Translation a polypeptide chain undergoes modifications. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
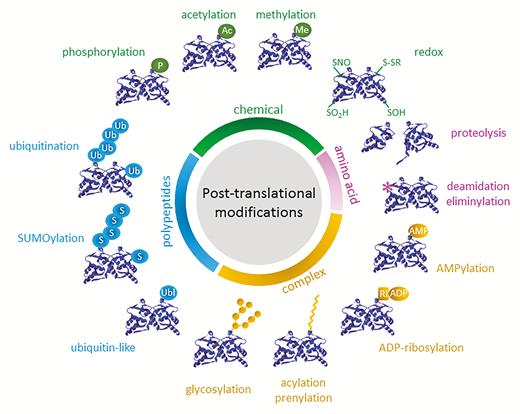
The post translational modifiactions can be enzymatic or covalent. Post-translational modifications are the chemical modifications a polypeptide chain receives after it is translated that convert it to the mature protein. Post-translational modifications change the chemical nature of the polypeptide chain through alterations to amino acid residues. The first post-translational modification applied to encoded polypeptides the oxidation of cysteine residues to form disulfide bridges is a natural one and was used to cyclise short peptides soon after the invention of phage display. Types Of Post Translational Modifications.
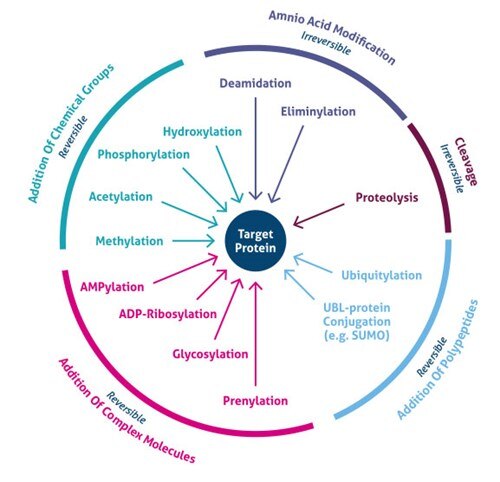 Source: ptglab.com
Source: ptglab.com
Polypeptide Chains Can Be Cleaved To Produce A Shorter And Functional Polypeptide. Post-translational modification PTM refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. Polypeptide Chains Can Be Cleaved To Produce A Shorter And Functional Polypeptide. The formation of disulfide bonds from cysteine residues may also be referred to as a post-translational modification. The first post-translational modification applied to encoded polypeptides the oxidation of cysteine residues to form disulfide bridges is a natural one and was used to cyclise short peptides soon after the invention of phage display.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
Removal of introns and splicing of exons C. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. The N-terminal Amino Acid Is Often Removed Or Modified. In the human body these PTMs increases the diversity and accuracy of proteins. Cleavage of a polypeptide into two or more chains During translation amino.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
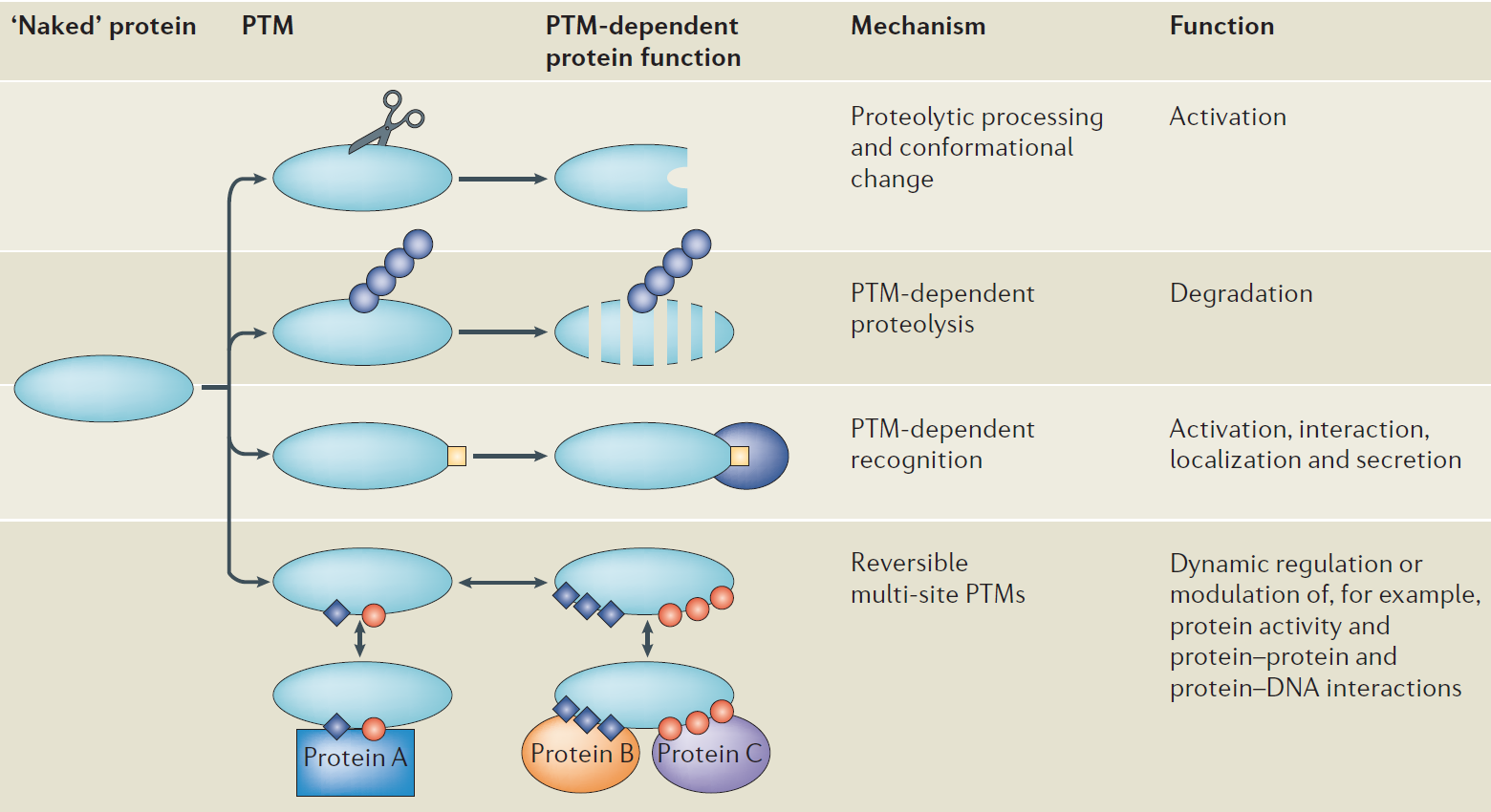
PTMs are important components in cell signaling as for example. Polypeptide Chains Can Be Cleaved To Produce A Shorter And Functional Polypeptide. Which of the following would NOT be a post-translational modification. All Of The Following Are Examples Of Posttranslational Modifications EXCEPT_____. Post-translational modification refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis.
 Source: creative-proteomics.com
Source: creative-proteomics.com
Post-translational modifications change the chemical nature of the polypeptide chain through alterations to amino acid residues. After Translation a polypeptide chain undergoes modifications. The formation of disulfide bonds from cysteine residues may also be referred to as a post-translational modification. Which of the following is a post-translational modification of a polypeptide. Polypeptide Chains Can Be Cleaved To Produce A Shorter And Functional Polypeptide.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Another common post-translational modification is cleavage or linking of parts of the protein itself. Post-translational modification refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. Which of the following is a post-translational modification of a polypeptide. Post-translational modifications take place in the ER and include folding glycosylation multimeric protein assembly and proteolytic cleavage leading to. Polypeptide Chains Can Be Cleaved To Produce A Shorter And Functional Polypeptide.
 Source: microbenotes.com
Source: microbenotes.com
PTMs are important components in cell signaling as for example when prohormones are converted to. Post translational modifications or PTMs are involved in modifying the protein structure after they have been translated according to information on the mRNA. Post-translational modification PTM refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. Which of the following would NOT be a post-translational modification. Which Of The Following Is Not A Type Of Post-translational Modification Or Regulation.
 Source: plantae.org
Source: plantae.org
Which of the following would NOT be a post-translational modification. Removal of introns and splicing of exons C. Cleavage of a polypeptide into two or more chains During translation amino. Post-translational modification refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. Post-translational modifications take place in the ER and include folding glycosylation multimeric protein assembly and proteolytic cleavage leading to.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. Removal of non-functional Introns D. During translation 20 different amino acids can be incorporated to make up a polypeptide chain. Adding A Sugar To A Polypeptide Alternative RNA Splicing Adding A Lipid To A Polypeptide Cutting Polypeptides Into Smaller Active Final Products. Addition of Acetate C.

Post translational modifications or PTMs are involved in modifying the protein structure after they have been translated according to information on the mRNA. In this lesson well talk about some of these modifications and why they help specify or change a. Post-translational modification PTM refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. Post-translational modifications are the chemical modifications a polypeptide chain receives after it is translated that convert it to the mature protein. Other forms of post-translational modification consist of cleaving peptide bonds as in processing a propeptide to a mature.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
PTMs are important components in cell signaling as for example. Post-translational modification refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. Signal-peptides may be cleaved parts may be excised from the middle of the protein or new covalent linkages may be made between cysteine or other amino acid side chains. The formation of disulfide bonds from cysteine residues may also be referred to as a post-translational modification. Polypeptides Can Be Degraded And Then Reassembled To Produce Entirely Different Sequenced Polypeptides.
 Source: drawittoknowit.com
Source: drawittoknowit.com
Post-translational modification refers to the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. The post translational modifiactions can be enzymatic or covalent. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. A protein is made up of a chain of amino acids also known as a polypeptide. In this lesson well talk about some of these modifications and why they help specify or change a.
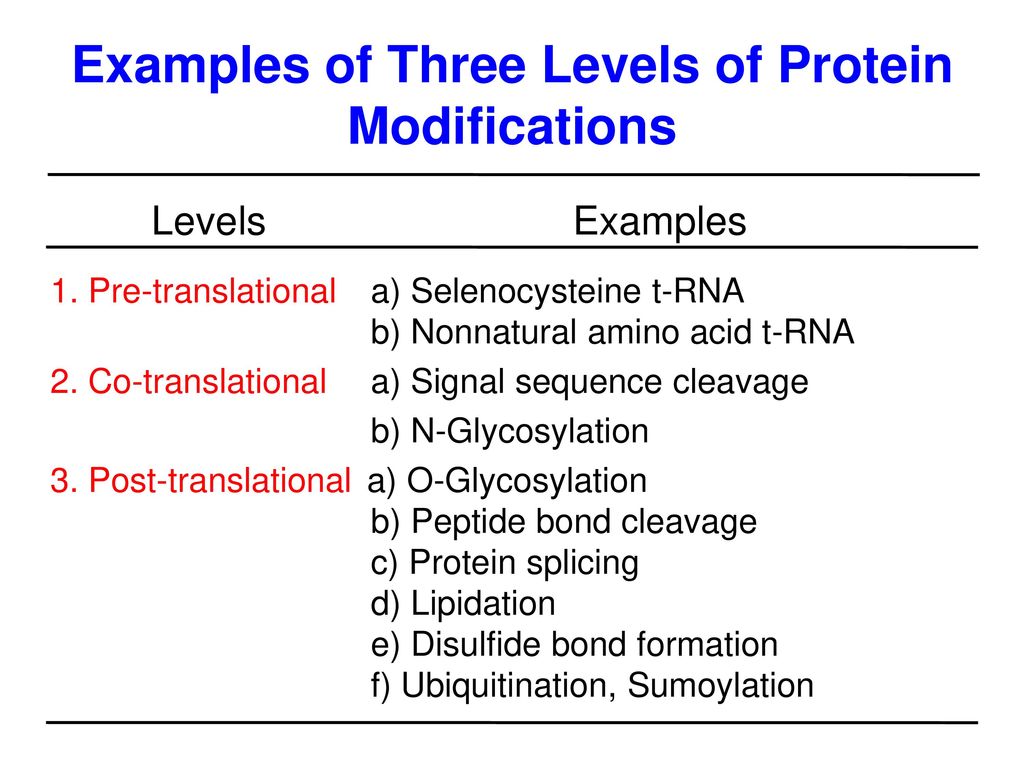 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Which of the following is a post-translational modification of a polypeptide. Post-translational modifications are the chemical modifications a polypeptide chain receives after it is translated that convert it to the mature protein. In the human body these PTMs increases the diversity and accuracy of proteins. Post-translational modifications can include cleaving a polypeptide or adding something to it. Which of the following would NOT be a post-translational modification.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title which of the following is a post translational modification of a polypeptide by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
Category
Related By Category
- Leatherman modification ideas
- Organizational behavior modification theory ideas
- Seamoth modification station location information
- Custody modification reasons information
- Kak shockwave modification information
- Subnautica cant place vehicle modification station information
- Loan modification while in chapter 13 information
- Behavior modification is based upon the principles of rewards and punishments advanced by ideas
- Modification lawyer information
- Z4 modification information